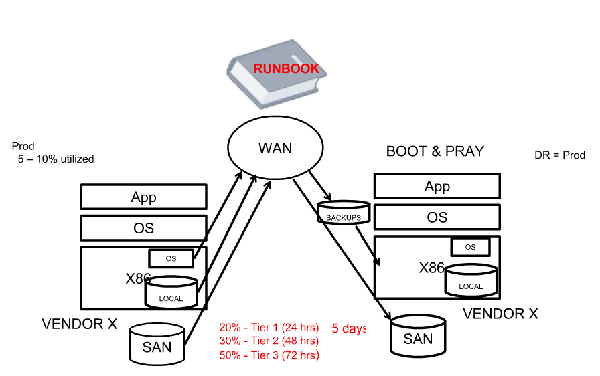
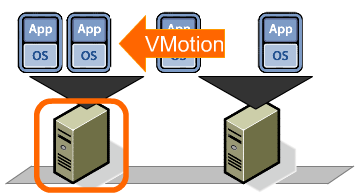
Many business’s IT infrastructures are based around this set up, with the operating system bound to a specific set of hardware and a specific Application bound to that OS. From there the server runs at about 5-10% of its capacity for most of the day with it peaking only during heavy usage. The data has to be backed up to a local SAN for recovery purposes, generally needing special software to be employed to ensure its being backed up fully and efficiently.
If this is a vital server and has a disaster recovery and business continuity plan implemented with it to ensure that downtime is kept as low as possible, then it will have an identical server installed for failover. This server is only used if the original server fails, but is still uses power and space. Not only that, but this server has to be the same identical model, containing the same hardware configuration, firmware, and local storage to ensure immediate complete compatibility with the original server. This adds cost as you need to have a second set of the hardware and it has to be that same model, limiting upgrade paths for the business.
This set up generally falls into the “Boot and Pray” model of disaster recovery, as the complexity of the set up causes the admin to hope that it works rather than being able to guarantee a smooth transition from server. This has to be done with every vital server that needs to have a redundant back up and each one has its own unique set up, creating a large amount of complexity that is involved with managing all these different machines. This complexity increases the company’s RTO and RPO and makes recovering a much larger ordeal.