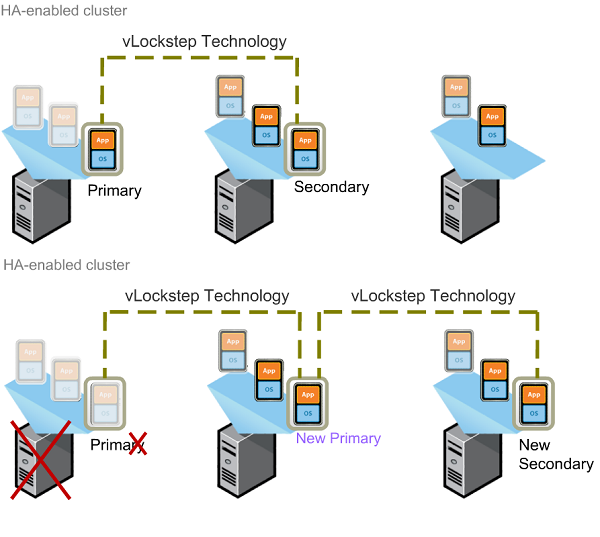
Is a server crash not an option for your company? Is having your server up and running the life and soul of your business? Then you may want to consider VMware’s Fault Tolerance (FT) feature. VMware Fault Tolerance is a step up from VMware High Availability (HA), with High Availability being VMware’s backup for a VM crash, if a server running a VM happens to go down then the host reboots on a different host. This allows for only a minute or two of downtime as the Virtual Machine starts up on a new server and the primary host that has crashed is restarted, if possible. This is extremely useful and can keep a business functioning with only a moment of downtime. What Fault Tolerance does is eliminate that couple minutes of downtime so that even if a server crashes, nothing is felt by the user. This feature gives companies that can’t stop functioning, even for a minute, the security they need to run their businesses.
How does FT work? Well with HA there is a primary server who runs the VM and a dedicated secondary host that is there in case of failure, if/when that failure occurs the secondary host is started and the VM is restarted on the new host. The failure is detected by using VMware’s heartbeat function that pings the server every second to ensure it is still active on the network, if the host stops responding it is considered to have failed and the VMs are moved to a new machine. FT continues this trend, but instead of waiting for a host to fail and then restart it uses vLockstep to keep both hosts in sync that way if one was to fail than the other would continue running without having the user notice the server failure. By sharing a virtualized storage, all the files are accessible to both hosts and the primary host updates the secondary host constantly in order to keep both hosts RAM in sync. FT has a few rules to ensure it works properly:
- Hosts must be in an HA cluster
- Primary and secondary VMs must run on different hosts
- Anti- affinity must be enabled (A configuration that ensures that the VM cannot be started on the same host)
- The VMs must be stored on a shared storage
- Minimum of 2 Gbps Nics, this is to allow vMotion and FT logging
- Additional NICs for VM and management network traffic
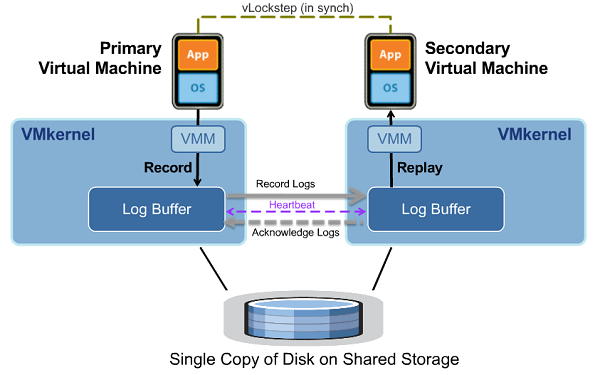
Using VMware’s FT helps IT build a better environment as dissimilar hardware can be used, allowing the IT department better upgrade options and allows repurposing of older existing hardware. Now a server that is on its last leg can still be used until it fails without worry about it affecting business when it finally fails. Fault Tolerance is a complicated set up and takes multiple servers which increase power consumption and parts needed to ensure that the system doesn’t ever fail, but if you need to ensure that you systems never go down it is the only way to go.
For more information visit VMwares FAQ on FT






